Microsoft developed Active Directory (AD) to provide authentication and authorization for a broad range of identity-related services. AD also provides a framework in which certificate services, federation services, lightweight directory services, rights management services, etc. run. AD was not built to integrate into Linux and Mac, into web-based applications, or the cloud. LDAP and RADIUS are the best active directory alternatives for Linux and Mac.

An LDAP Server is where the directory is situated.
An LDAP Client is the system that contacts the LDAP Server to fetch the directory entries.
An LDAP session is when an LDAP client connects to the LDAP server.
Add operation inserts a new entry to the directory server database. If a DN already exists in the directory, a new entry will not be added.
Bind operation allows an LDAP client to authenticate to the LDAP server when an LDAP session is started.
Delete operation removes an entry when an LDAP client transmits a delete request to the LDAP Server.
Search operation is used to read and search for entries.
Modify operation is used by LDAP clients to request the LDAP Server to make changes to existing entries.
Modify DN operation uses a new RDN to modify the new parent’s DN.
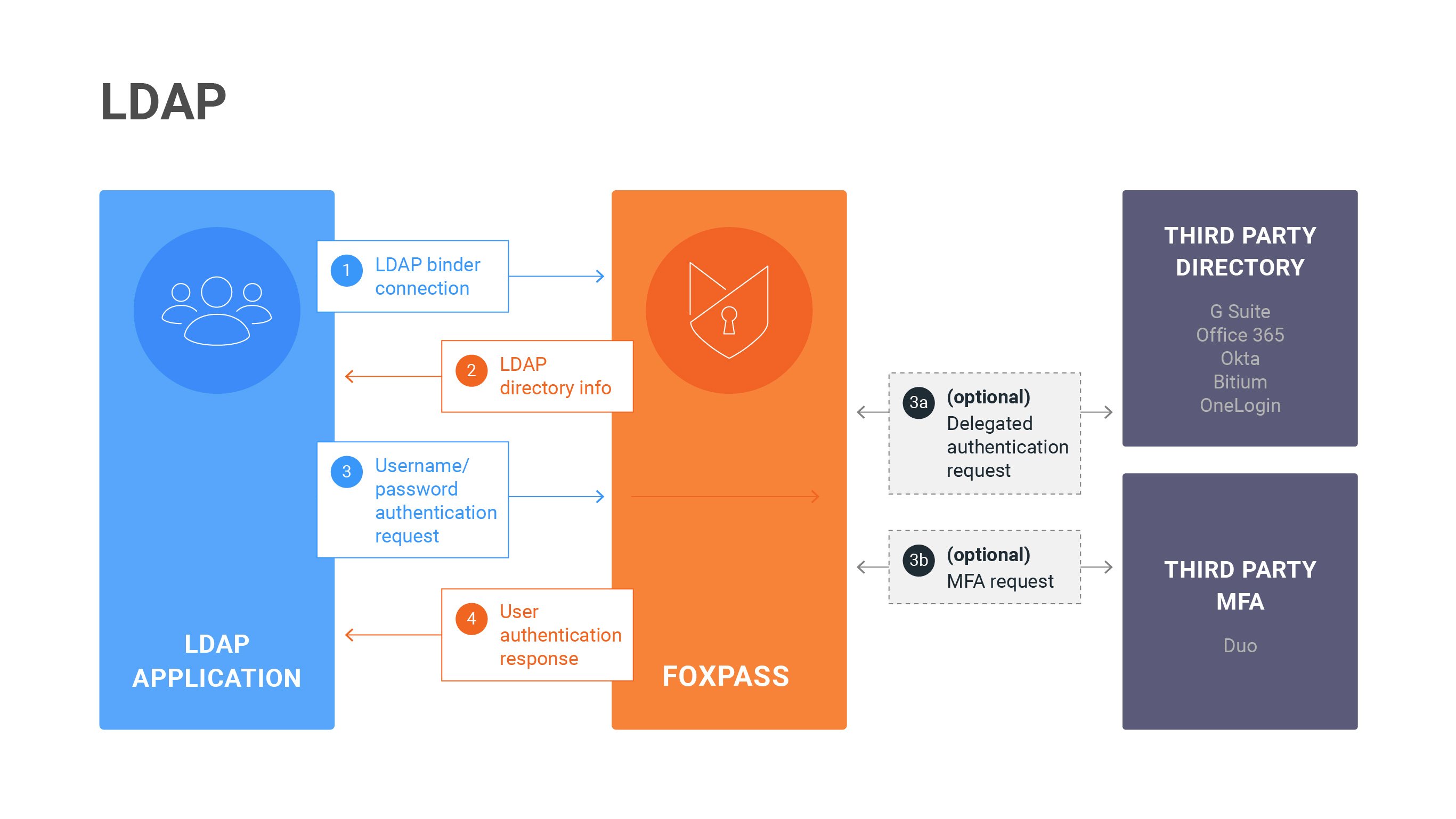
To authenticate a user with an LDAP, it is important to obtain the user’s DN as well as their password. In a login form, users typically enter their username or email address. An LDAP client sends a request to the LDAP Server and uses DN resolution to take the user’s name or email, run a search against the user entries and find the matching DN.
If the username is matched with the DN, the LDAP Server authenticates the user and grants access to the system. If the username is not matched, authentication fails.
Using FoxPass LDAP as an Active Directory alternative,You can use FoxPass LDAP as an Active Directory alternative for Linux and Mac. Your application can integrate with Foxpass to bind with an anonymous LDAP Binder and perform a search to get a list of users and groups from an LDAP Server. SSH key-based logins use alternative methods of authentication.

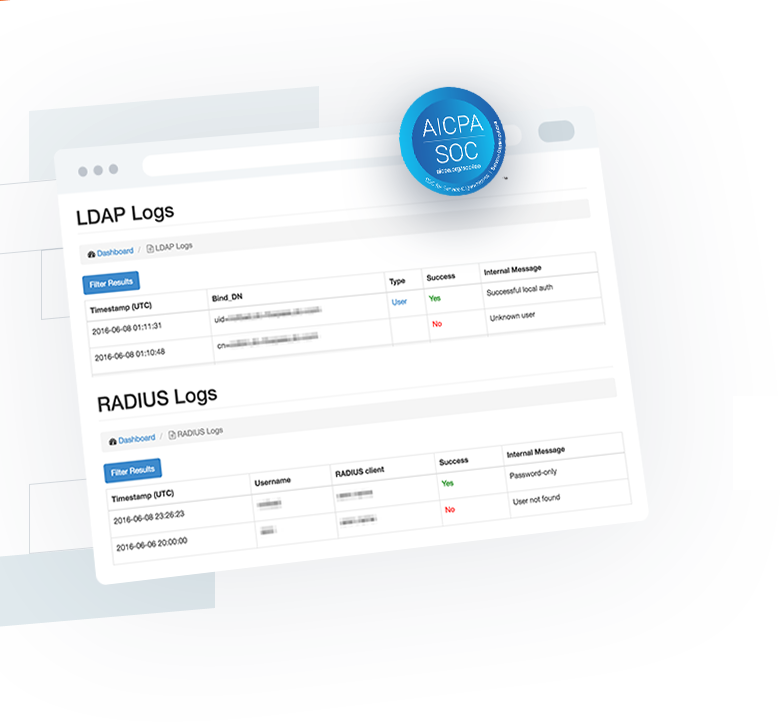
Using Foxpass, you can also debug and troubleshoot issues with your LDAP connection with ease. You can check LDAP logs to ensure that the configuration is correct.
Foxpass also offers exceptional support. For any issues related to the LDAP connection, you can easily contact help@foxpass.com.
Access request manages authentication and authorization.
Accounting request manages accounting.
User is unconditionally denied access to all requested resources.
User is required to provide additional information such as secondary password, token, card, or PIN.
User is granted access.

After network access is granted to the user, the Accounting-Start request packet is sent by the NAS to the Radius Server to start the accounting of the user's network access. When the user's network access is finished, the Accounting-Stop request is issued by the NAS to the RADIUS server. This is used for billing purposes.
Using FoxPass RADIUS as an Active Directory alternative
You can use Foxpass Radius as an active directory alternative for Linux and Mac. The process involves:
Using Foxpass, you can also debug and troubleshoot issues with your RADIUS connection with ease. You can check RADIUS logs to ensure that the configuration is correct.
Foxpass also offers exceptional support. For any issues related to the connection, you can contact help@foxpass.com.
Use your G Suite or Office 365 account, or sign up with your email address.
(Have an account already? Click here to log in.)
By signing up, you agree to our terms of use and privacy policy.