Role-Based Access Control, or RBAC for short, is resource access-restricted based upon the user’s job title or role within an organization.
For example: you wouldn’t want John in accounting to have the same access privileges to your company’s infrastructure that Susie the engineer does.
RBAC makes it incredibly easy for a manager to designate what employees are granted permissions to perform certain operations on both a broad and finely-tuned, granular level.
The diagram below is a basic overview of RBAC:
.png?width=687&name=RBAC_blog_diagram%20(2).png) RBAC Pros
RBAC Pros
- Granular visibility
- Simplifies network security management
- Access to only what users need, when they need it
Why Use RBAC?
- Reduce employee downtime due to access issues
- More efficient provisioning
- Implementation of Identity & Access Management policies (make sure only the right people have access to the correct systems)
2 Examples of RBAC
- Providing access to developers or engineers vs admins or sales people
- Choosing who has more or less access in an educational institution setting, such as students and faculty. Students would get access to student-designated Wi-Fi® and the student drives, faculty would get higher level staff-specific access, plus access to what students have.
Additional knowledge on Role-Based Access Control
3 Primary Rules for RBAC:
- Role assignment: A user can exercise a permission only if the subject has been assigned a role.
- Role-based authorization: A user’s active role must be authorized. With rule 1 above, this rule ensures that users can take on only roles for which they are authorized.
- Permission authorization: A user can make use of certain permissions only if the user is authorized to that specific permission, according to their role assignment in the role-based structure hierarchy. This rule specifies that 1 & 2 have been exercised.
RBAC Conventions
|
Designation |
Term |
Meaning |
|
S |
Subject |
A person or automated agent |
|
R |
Role |
What the person does |
|
P |
Permission |
An approval mode of access to a resource |
|
SE |
Session |
Mapping involving S, E, and/or P |
|
SA |
Subject Assignment |
|
|
PA |
Permission Assignment |
|
|
RH |
Role Hierarchy |
Foxpass Offers RBAC Without the Hassle
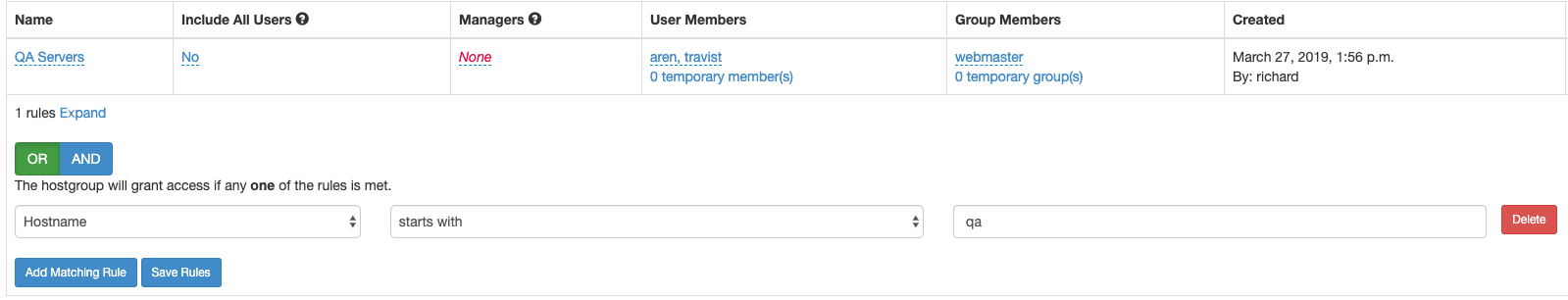
Foxpass offers easy Role-Based Access Control at the click of a button using our Host Groups feature which restrict user or group SSH access to subsets of your hosts.
Host Groups can filter hosts by hostname, AWS Connection Name, AWS VPC ID, AWS Subnet ID, or AWS Tag:
Simplify your network security using RBAC and have your infrastructure secured in minutes, not weeks or months.

.png)



